Economics Terms A-Z
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns
Read a summary or generate practice questions using the INOMICS AI tool
The production of goods and services requires the input of various factors of production. The law of diminishing marginal returns states that as the input of a factor of production increases, ceteris paribus, the additional output from each additional unit of that input decreases.
For example, the production of fruit and vegetables requires sufficient land of the appropriate type with water and sunlight. It also requires labor and machinery to plant, cultivate and harvest the crop, as well as packaging and people or machines to present the produce for sale. Similarly, the production of a school education requires trained teachers and administrators, books and other learning materials, as well as buildings and/or other space to host the education.
Applied to the first example of producing fruit and vegetables, the law of diminishing marginal returns implies that increasing the input of one factor such as land, while holding the input of the other factors (labor and machinery) constant, will increase the amount of the fruit and vegetables produced at a decreasing rate as more land is added. That is, each additional square meter of land, for fixed levels of the other factors, will yield smaller increases in output of fruit and vegetables.
Applied to the second example, the first teacher or the first book will add much to the education provided. But, each subsequent teacher employed without increasing the availability of learning materials, administrators, or physical space, will expand education at a decreasing rate.
The law of diminishing marginal returns can be represented graphically in two dimensions with the (total) return R as a concave function of the input i of a single factor of production (while the inputs of other factors are held constant). As more of this single factor of production is employed, for the same unit increases in input Δi, the additional (i.e. marginal) return diminishes ΔR” < ΔR’ < ΔR:
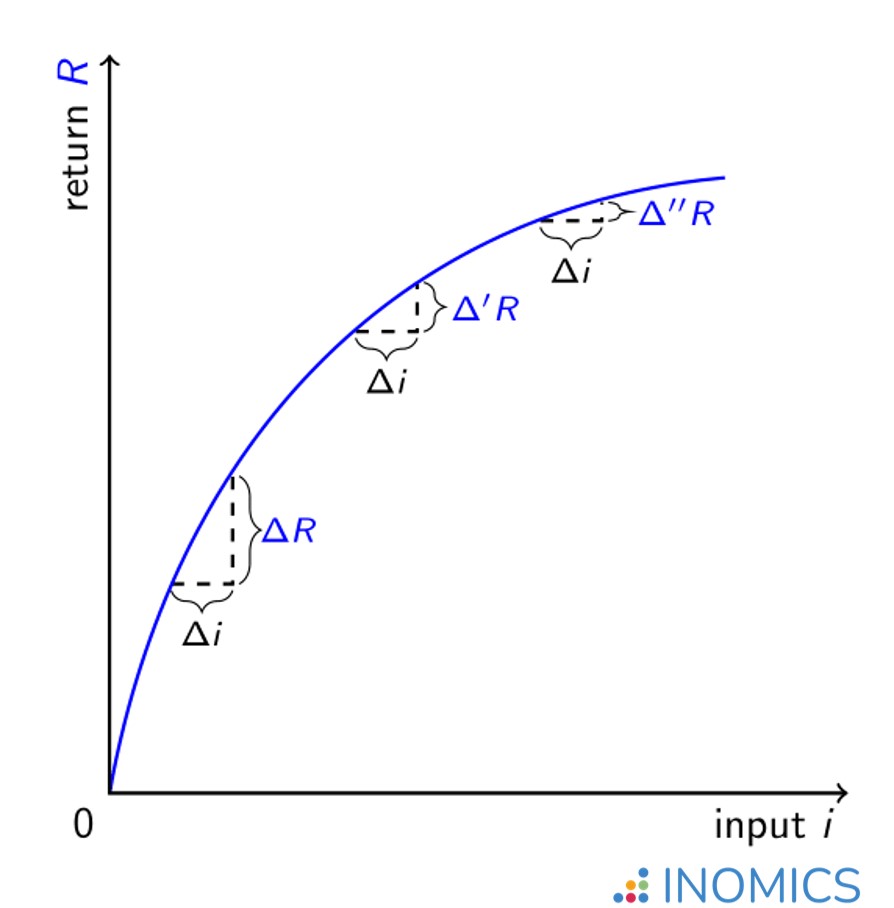
Figure 1: Law of diminishing marginal returns for a revenue function
At first glance, the law of diminishing marginal returns might seem to contradict the concept of economies of scale whereby increasing inputs should generate increasing, not diminishing, returns. Note however that the law of diminishing marginal returns relates specifically to varying the input of a single factor of production while holding all other factors constant.
As such, it implies that different factors of production are not perfect substitutes for each other; instead, there is a degree of complementarity between input factors. You might be able to bake a larger cake by adding a bit more flour but if you do not also increase the quantities of eggs, sugar and oil the cake is liable to become dry and tasteless!
Its description as a “law” makes the law of diminishing marginal returns sound grand and as indisputable as a law of physics. In fact, it can be considered more of an assumption of the theory of production. As with all assumptions, it is open to challenge.
Indeed, some economists argue that marginal returns to input factors are increasing at low levels of production. The law of diminishing marginal returns thus may not apply to all forms of production and therefore should be treated with caution.
Further reading
The economist Stanley Brue presents a critical history of the law of diminishing marginal returns in economic thought, highlighting the lack of empirical evidence to support it, in “Retrospectives: The Law of Diminishing Returns” (Journal of Economic Perspectives, 1993).
Good to know
The law of diminishing marginal returns does apply to learning, and in particular to exam preparation: the first hour spent cramming for an exam is generally more productive than subsequent hours. It is important to balance individual learning with dialogue, discussing and questioning the content with others. Experimentation with different input quantities can help you to maximize the returns to your education!
-
- Conference
- Posted 2 weeks ago
46th RSEP International Conference on Economics, Finance and Business
Between 17 Apr and 18 Apr in Paris, France
-
- PhD Candidate Job
- Posted 2 weeks ago
Researcher in Economic Theory and Policy, Behavioural Economics, Empirical Economics, or Econometrics (75 %; EG 13 TV-L)
At Düsseldorf Institute for Competition Economics (DICE) - University of Düsseldorf in Düsseldorf, Germany
-
- PhD Program
- Posted 5 days ago
Ph.D. in Finance, fully funded
at Leibniz Institute for Financial Research SAFE in Frankfurt am Main, Germany













